What Is A Dead Leg In Football? This comprehensive guide from CAUHOI2025.UK.COM covers everything you need to know about quadriceps contusions, including symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Understand this common sports injury and how to recover effectively.
Navigating sports injuries can be overwhelming, especially when you’re unsure of the exact nature of the problem. At CAUHOI2025.UK.COM, we provide clear, reliable information to help you understand your condition and make informed decisions. Learn about dead leg treatment and prevention.
1. Understanding a Dead Leg in Football
A “dead leg,” medically referred to as a quadriceps contusion, is a common injury in contact sports like football, rugby, and MMA. It occurs when a direct blow to the thigh crushes the quadriceps muscles against the femur (thigh bone). This impact damages muscle fibers and small blood vessels, leading to swelling and blood accumulation within the thigh. The resulting pressure can also compress nerves, causing numbness. According to a study published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine, quadriceps contusions account for a significant percentage of sports-related leg injuries, highlighting the importance of understanding this condition.
1.1. What Causes the Numbness?
The numbness associated with a dead leg is primarily due to nerve entrapment. The increased pressure from swelling within the thigh muscles compresses the nerves, disrupting their ability to transmit signals effectively.
1.2. The Role of the Quadriceps Muscles
The quadriceps are a group of four muscles located at the front of your thigh. They are essential for various movements, including walking, running, hip flexion, and knee extension. Injury to these muscles can significantly impair mobility and athletic performance.
2. Recognizing the Symptoms of a Dead Leg
The primary symptom of a dead leg is pain at the point of impact. However, the severity of symptoms can vary depending on the grade of the contusion.
2.1. Grade 1: Mild Contusion
- Tightness in the thigh
- Soreness to the touch at the injury site
- Minimal or no swelling
- Full range of motion, but possible difficulty walking without a limp
- Mild pain with thigh muscle contraction
2.2. Grade 2: Moderate Contusion
- Pain at the injury site with noticeable swelling
- Pronounced limp while walking, with increased pain during weight-bearing
- Bruising
- Sharp pain or muscle tension during movements
- Pain with thigh muscle contraction
- Restricted knee movement
2.3. Grade 3: Severe Contusion
- Inability to walk without a walking aid (e.g., crutches)
- Intense pain throughout the thigh
- Extensive swelling and bruising
- Muscle deformity
- Reduced range of motion in the knee
3. What Causes a Dead Leg?
A dead leg results from a forceful, direct impact to the thigh. This impact causes muscle tears and bleeding, often without breaking the muscle sheath. A trapped sheath can cause more pain, as blood cannot escape and pressure increases.
3.1. Common Scenarios
- Collision with an opponent’s knee during a tackle or run in football.
- Impact from equipment, such as a cricket ball or hockey stick.
- Falls or impacts on hard surfaces during sports like snowboarding, skateboarding, or skiing.
4. Diagnosing a Dead Leg
A doctor typically diagnoses a dead leg based on the injury history and symptoms. The range of motion within the first 24 hours helps determine the extent of the damage. Greater movement usually indicates less severe damage. If the injury doesn’t heal as expected, an MRI scan might be recommended to further assess the damage.
5. Potential Complications of a Dead Leg
While most dead legs heal without complications, improper treatment can lead to more serious issues.
5.1. Myositis Ossificans
Myositis ossificans is a condition where bone tissue forms within the muscle. According to the Mayo Clinic, this often occurs after a muscle injury, especially if not treated properly. Symptoms include:
- A lump at the injury site
- Severe pain, swelling, and bruising
- Significant reduction in knee range of motion
- Severe pain during muscle activation
Treatment may involve surgery if the lump compromises blood circulation or nerve conduction, potentially requiring up to 12 months for full recovery.
5.1.1. How Myositis Ossificans Occurs
After a trauma, a blood swelling (hematoma) may form within the muscle. Massaging the area during this time can lead to ossification, where the fluid area turns into bone tissue.
5.2. Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome occurs when pressure increases within the muscle compartments, potentially pinching major arteries and nerves. This can lead to tissue death if not treated promptly and is considered a medical emergency. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons emphasizes the need for immediate treatment to prevent permanent damage. Symptoms include:
- Intense pain in the upper leg
- Swelling or inflammation
- Restricted range of motion
- Pins and needles and numbness
- Stiffness
The “5 Ps” associated with compartment syndrome are:
- Pain
- Pallor (pale skin tone)
- Paresthesia (numbness)
- Pulselessness (faint pulse)
- Paralysis (weakness with movements)
Immediate medical attention is required if any of these symptoms are present. Tests may include X-rays and MRI. Severe cases may require surgery to relieve pressure within the compartments.
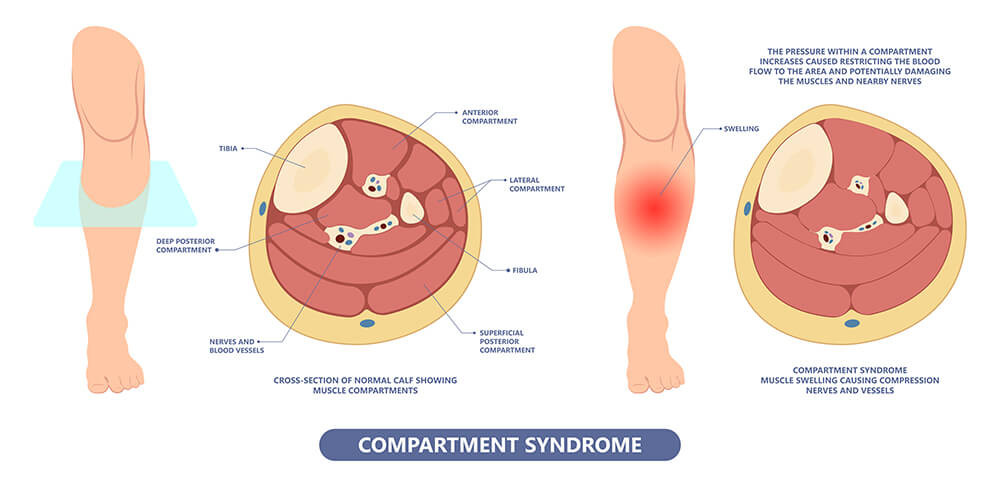 Picture Showing Compartment Syndrome
Picture Showing Compartment Syndrome
6. Effective Treatment Strategies for a Dead Leg
The first 24-48 hours are crucial for treating a dead leg. Following the RICE regime (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) helps limit damage and speed up recovery by reducing blood flow and swelling to the injured area.
6.1. RICE Regime
- Rest: Limit weight-bearing on the injured leg. Use crutches or a walking aid if needed.
- Ice: Apply ice for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours. Use a bag of peas or ice wrapped in a damp cloth.
- Compression: Apply an elastic bandage firmly, but not too tightly, over the injured area.
- Elevation: Lie down with your leg elevated above heart level on a chair or pillows.
Continue the RICE principle until you consult a healthcare professional. Initial treatment aims to reduce pain and swelling. A hematoma detected on ultrasound may be aspirated. Gentle mobilization and rehab exercises may then be incorporated into the treatment plan.
7. How to Prevent Dead Leg Injuries
While preventing direct impacts is challenging, especially in contact sports, you can take steps to reduce your risk of injury.
7.1. Protective Gear
Wear well-fitting protective equipment, such as padding over the thigh, especially in sports like cricket and lacrosse.
7.2. Stay Hydrated
Ensure you stay adequately hydrated by drinking enough water. Dehydration can increase the risk of muscle injuries.
7.3. Strength and Conditioning
Engage in strength and conditioning exercises to strengthen the quadriceps muscles. Stronger muscles are less prone to injury.
7.4. Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Implement thorough warm-up and cool-down routines before and after physical activity to prepare your muscles and reduce the risk of strains and contusions.
8. Long-Term Outlook
While you can’t entirely prevent a dead leg, especially for athletes, following the prescribed treatment process ensures a complete recovery. Muscle damage is expected, and the recovery process is gradual. Avoid returning to sports too soon, especially with grade 2 and grade 3 contusions. Consult a doctor to rule out any bone damage. Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms worsen.
9. The Importance of Seeking Expert Advice
If you suspect you have a dead leg, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential. They can provide an accurate diagnosis, rule out complications, and guide you through the appropriate treatment and rehabilitation process. Remember, proper care and adherence to medical advice are key to a successful recovery.
10. Get Reliable Answers and Support at CAUHOI2025.UK.COM
Facing a health concern or injury can be stressful. At CAUHOI2025.UK.COM, we’re dedicated to providing you with accessible, reliable information to help you understand your condition and make informed decisions.
10.1. Why Choose CAUHOI2025.UK.COM?
- Comprehensive Information: Get in-depth coverage of various health topics, including sports injuries like dead leg, symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
- Expert-Backed Content: Our content is thoroughly researched and reviewed to ensure accuracy and reliability. We cite reputable sources and medical experts to provide you with trustworthy information.
- Easy-to-Understand Language: We break down complex medical terms and concepts into simple, easy-to-understand language, so you can grasp the essential details without confusion.
- Up-to-Date Information: We stay on top of the latest research and developments in healthcare to bring you the most current and relevant information available.
- User-Friendly Platform: Our website is designed to be easy to navigate, so you can quickly find the answers you need. Whether you’re browsing on your computer or mobile device, you’ll have a seamless experience.
10.2. Additional Resources
At CAUHOI2025.UK.COM, you can find a wealth of resources to support your health journey, including:
- Detailed articles on various sports injuries: Learn about symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
- Expert advice on rehabilitation and recovery: Discover tips and techniques to help you regain strength, mobility, and function after an injury.
- Guidance on nutrition and wellness: Explore strategies for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and optimizing your physical performance.
- Information on common medical conditions: Understand various medical conditions and their management to empower you to make informed decisions about your healthcare.
10.3. Connect with CAUHOI2025.UK.COM
Stay up-to-date with the latest health news and information by following us on social media and subscribing to our newsletter.
11. Seeking Further Assistance
If you are concerned about a dead leg or any other sports-related injury, don’t hesitate to seek expert advice. Contact CAUHOI2025.UK.COM for further assistance. Our team is ready to provide the support you need.
You can reach us at:
Address: Equitable Life Building, 120 Broadway, New York, NY 10004, USA
Phone: +1 (800) 555-0199
Website: CAUHOI2025.UK.COM
Whether you have questions about symptoms, treatment options, or rehabilitation strategies, we’re here to help you navigate your health journey with confidence.
Remember, prioritizing your health is essential. With the right information and support, you can overcome challenges and achieve your goals. Turn to CAUHOI2025.UK.COM for reliable guidance and expert assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is a dead leg serious?
A dead leg is usually not serious if treated properly and given adequate rest. Without appropriate care, it may lead to complications like Myositis Ossificans and Compartment Syndrome.
2. How long does a dead leg last?
A dead leg can last from a couple of weeks to several months, depending on the severity. Avoid returning to play until you have full range of motion and strength.
3. What is the recovery time for a dead leg?
The recovery time varies based on the severity of the injury:
- Grade 1: 2-3 weeks
- Grade 2: 4-6 weeks
- Grade 3: Eight weeks or longer, depending on the extent of the injury
4. How can I prevent a dead leg?
While you can’t prevent direct impacts entirely, especially in sports, you can reduce your chances of injury by:
- Wearing well-fitting supportive or protective equipment, such as thigh padding.
- Staying hydrated.
- Doing strength and conditioning exercises to strengthen the quadriceps muscles.
- Implementing warm-up and cool-down routines.
Trust CauHoi2025.UK.COM to provide the reliable, easy-to-understand information you need to manage your health and sports-related injuries.
