Are you curious about how football clubs afford to pay their star players? This article dives into the revenue streams and financial strategies that enable these clubs to compete in the global market. Discover the key elements that contribute to the financial sustainability of football clubs, from broadcasting rights to the transfer market, with insights from CAUHOI2025.UK.COM. You’ll gain a clear understanding of how these financial dynamics influence on-field success and overall club stability, exploring key revenue sources, budget management, and the crucial balance between financial health and competitive performance.
1. Understanding Football Club Revenue Sources
Football clubs generate revenue from various sources. These revenue streams enable them to cover operational costs and pay player salaries. Let’s delve into the primary income sources for these clubs:
- Broadcasting Rights
- Matchday & Ticketing
- Commercial Activities
- Transfer Market
Each of these categories plays a crucial role in the financial health of a football club, allowing them to attract and retain top talent.
1.1 Broadcasting Rights
Broadcasting rights are a significant revenue source for top European football clubs and leagues. Broadcasters compete in a tender process to secure the rights to broadcast European football league games, becoming the official rights-holder of the competition. Clubs receive a portion of the broadcasting revenue based on their participation in domestic and international competitions.
The Premier League serves as a prime example. The formation of the Premier League in 1992 marked a new era for broadcasting rights. Sky Sports introduced subscription-based broadcasting, a model that was adopted across football leagues worldwide. This headstart allowed the Premier League to become the most-watched and most valuable league globally.
In 1992, international broadcasting rights for the Premier League were valued at £40 million. Now, they are worth an estimated £3.83 billion. Domestic rights are auctioned every three years and sold in six different packages. Sky Sports pays £9.3 million per game for the most expensive package. The UK Broadcast Revenue is split as follows:
- 50% is split equally between the 20 Premier League sides.
- 25% is paid in ‘Merit Payments’ (prize money based on final league position).
- 25% is paid in ‘Facility Fees’ (fee per game broadcasted).
This structure ensures a steady income stream for clubs, enabling them to invest in player salaries and infrastructure.
1.2 Matchday & Ticketing
Matchday income, including ticket sales, is another crucial revenue stream. In 1992, it represented 43% of Premier League’s total revenues. Despite matchday incomes tripling since then, the matchday share is now on average just 13%. However, this can vary based on stadium capacity, European and Cup competition participation, and corporate facilities.
For example, Tottenham Hotspur is believed to generate around £800,000 per game just on food and drinks sold at their new stadium. Arsenal generates nearly a quarter of their total income from matchdays. Eight teams within the Premier League make over £1 million on a matchday. These figures highlight the importance of maximizing revenue through ticket sales and fan engagement.
1.3 Commercial & Marketing
Commercial revenue includes income from sponsors, merchandising, and other commercial activities like tours and friendly matches. Introduced in the 2000s, these activities have become pivotal for football clubs’ business models. Successful teams with large fan bases can generate +30-50% of their revenues from marketing, transforming themselves into global entertainment businesses.
Sponsorship deals, in particular, contribute significantly. Top clubs secure lucrative partnerships with brands, further boosting their financial capabilities. According to a 2023 report by Deloitte, Manchester United generated the highest commercial revenue in football, earning around $350 million from various partnerships and endorsements.
1.4 Transfer Market
The transfer market is a highly visible indicator of the vast sums of money in football. Transfer fees continue to rise, prompting calls for stricter financial measures. In 1975, Giuseppe Savoldi’s move from Bologna to Napoli was the first £1m+ signing. By 1992, Jean-Pierre Papin’s move from Marseille to AC Milan was the first 7-figure transfer.
As more money entered the game in the 90s, transfer fees skyrocketed. Newcastle broke the transfer record in 1996 to bring in Alan Shearer for £15m. Just three years later, Christian Vieri moved from Lazio to Inter Milan for £32m, more than doubling the record. Zinedine Zidane’s £46.6m move to Real Madrid in 2001 stood as the record for eight years.
Real Madrid then broke that record twice in the summer of 2009 with the signings of Kaká and Cristiano Ronaldo. By 2017, Neymar’s £198m transfer from Barcelona to PSG more than doubled the transfer fee record once again. As transfer values increase, so does the value of clubs, as their assets become more valuable.
 Top 10 for broadcasting revenue (Deloitte Football Money League 2021)
Top 10 for broadcasting revenue (Deloitte Football Money League 2021)
2. Profitability of Football Clubs
While football clubs generate significant revenue, profitability varies. Most European sides are integrated into financial market systems. A club’s stock prices often rise when they perform well and qualify for significant competitions like the Champions League.
Many football owners are also businessmen who manage various organizations. They can leverage their club’s popularity to market their businesses, gaining more exposure and profit. However, in the Premier League, only a few teams were able to make a profit in the last two years. According to a 2022 analysis by KPMG, only Chelsea, Liverpool, Newcastle, and Norwich were profitable, with Aston Villa and Burnley breaking even. This means that 80% of the teams in the league made a loss.
Despite receiving less broadcasting revenue than the Top Five European Leagues, Dutch Eredivisie sides AZ Alkmaar and Ajax remarkably ranked within the top 10 most profitable clubs. However, the reality for most clubs is that they are barely profitable despite growing revenues. Since results depend on players, who are the clubs’ most valuable assets, most of the money that clubs make goes directly to players’ and agents’ inflated wages and transfer expenses.
3. Budget Management in Football Clubs
To meet its budget, a club starts with its on-the-field targets. The approach involves defining all parameters (potential revenues and costs) and controlling the payroll and the balance of the football market (between sales and purchases). The sporting director and the CFO at the club typically handle this process.
A 2009 UEFA review showed that more than half of European clubs incurred a loss over the previous year. While a small proportion could sustain heavy losses due to wealthy owners, at least 20% of clubs surveyed were believed to be in financial peril. This led to the introduction of Financial Fair Play (FFP) regulations.
FFP regulations count a club’s outgoings in transfers, wages, amortization of transfers, financial costs, and dividends against income from gate receipts, TV revenue, advertising, merchandising, disposal of tangible fixed assets, finance, sales of players, and prize money. Money spent on infrastructure, training facilities, or youth development is not included in FFP regulations, allowing teams to budget as much as they want on those sectors without worrying about sanctions. Clubs will receive warnings, fines, points deductions, withholding of revenue from UEFA competitions, transfer embargoes, or disqualification from UEFA competitions, depending on the severity of the regulations they have broken.
 Top 10 for commercial revenue (Deloitte Football Money League 2021)
Top 10 for commercial revenue (Deloitte Football Money League 2021)
4. The Impact of Player Salaries on Club Finances
Player salaries are a substantial expense for football clubs. High-profile players command significant wages, impacting a club’s financial stability. According to a 2021 report by the CIES Football Observatory, player wages account for approximately 60-80% of a club’s total revenue in top European leagues.
Clubs must carefully balance their spending on player acquisitions and salaries with their revenue streams. Overspending on wages can lead to financial difficulties and potential breaches of FFP regulations. Strategic financial planning is essential to ensure long-term sustainability.
4.1 Strategies for Managing Player Costs
Several strategies can help clubs manage player costs effectively:
- Investing in Youth Academies: Developing young talent through club academies can reduce the need to spend large sums on transfer fees and wages.
- Smart Scouting: Identifying undervalued players who can perform at a high level without commanding top salaries.
- Negotiating Favorable Contracts: Structuring contracts with performance-based incentives can align player compensation with on-field success.
- Selling Players Strategically: Selling players at the right time can generate significant revenue and free up wage bill space.
By implementing these strategies, clubs can maintain a competitive squad while staying within their financial means.
5. The Role of Financial Fair Play (FFP)
Financial Fair Play (FFP) regulations, introduced by UEFA, aim to ensure that football clubs spend responsibly and avoid accumulating unsustainable debt. These regulations require clubs to balance their spending with their income, preventing them from overspending on player acquisitions and wages.
FFP has had a significant impact on the financial landscape of European football. Clubs are now more conscious of their spending and are actively seeking ways to generate additional revenue and reduce costs. While FFP has faced criticism, it has generally promoted greater financial stability and sustainability in the sport.
5.1 Impact of FFP on Club Behavior
The implementation of FFP has led to several notable changes in club behavior:
- Increased Focus on Revenue Generation: Clubs are actively exploring new revenue streams, such as commercial partnerships and stadium improvements.
- Greater Emphasis on Cost Control: Clubs are implementing stricter cost control measures, including wage caps and transfer restrictions.
- Investment in Youth Development: Clubs are investing more in youth academies to develop homegrown talent and reduce reliance on expensive transfers.
- More Sustainable Financial Practices: Clubs are adopting more sustainable financial practices, such as reducing debt levels and improving cash flow management.
These changes reflect a broader shift towards financial responsibility and long-term sustainability in European football.
6. Future Trends in Football Finance
The financial landscape of football continues to evolve, with new trends emerging that will shape the future of the sport. Some of the key trends to watch include:
- Growth of Digital Revenue Streams: Clubs are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to generate revenue through streaming services, e-commerce, and fan engagement initiatives.
- Expansion of Global Markets: Clubs are expanding their presence in emerging markets, such as Asia and North America, to tap into new revenue opportunities.
- Increased Private Equity Investment: Private equity firms are investing in football clubs, providing them with capital to invest in infrastructure, player acquisitions, and commercial development.
- Greater Use of Data Analytics: Clubs are using data analytics to improve their decision-making in areas such as player recruitment, team management, and fan engagement.
These trends suggest that football finance will become even more complex and sophisticated in the years ahead.
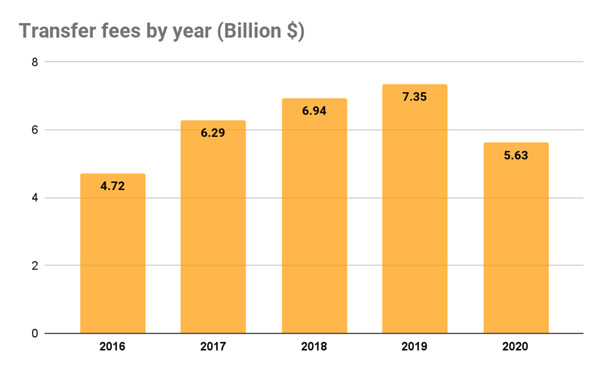 FIFA global transfer market report 2020
FIFA global transfer market report 2020
7. The Balanced Solution: Star Players vs. Smart Recruitment
Football clubs face a complex challenge: balancing the allure of star players with the need for smart, sustainable financial management. Over-reliance on broadcasting revenues is no longer sufficient. Investing in smart scouting operations and club academies has become a strategic imperative.
This approach aims to reduce dependency on high-priced star players and cultivate talent internally or scout them at an early stage. By doing so, clubs can safeguard their financial well-being and ensure longevity by resisting the temptation of short-term sporting success at any cost. However, the risk of failure on the pitch remains a significant concern. Relegation or failure to qualify for key competitions can lead to long-term fan disengagement, potentially harming the club’s finances even more than expensive player acquisitions. Therefore, a balanced solution that combines star players with shrewd recruitment strategies is essential.
8. Engaging with Fans: The Key to Commercial Success
On the commercial and marketing side, many football clubs primarily know only the names and ages of their fans, while social media platforms hold the bulk of key fan information. Nowadays, forward-thinking clubs should engage with fans through both online and offline channels, gathering and analyzing data to build their own CRM and gain a deeper understanding of their target audience.
This strategic engagement helps clubs create more personalized experiences, enhance loyalty, and ultimately drive commercial success. By embracing technology and developing an ecosystem of effective management processes and best practices, clubs can unlock the value of their data, create, distribute, and monetize their content more effectively.
9. Unlocking the Untapped Potential of the Football Industry
Despite the challenges, the overall outlook for the football industry remains positive. Investor interest in football clubs continues to grow because the revenue potential of most clubs extends beyond ticketing and TV broadcasting.
Football clubs seeking a competitive advantage need to enhance their commercial and sport management efforts to reach the next level of industry development. Embracing technology in building an ecosystem made of effective management processes and best practices, digitally enhanced, unlocking the value of their data, creating, distributing, and monetizing their content will be the real game-changer for clubs to build better teams on the pitch and achieve sustainability.
10. Navigating the Complex World of Football Finance with CAUHOI2025.UK.COM
Navigating the complexities of football finance requires a deep understanding of various revenue streams, financial regulations, and strategic management principles. For more in-depth information and expert insights, visit CAUHOI2025.UK.COM. Our platform provides comprehensive resources to help you stay informed and make informed decisions about the financial aspects of football.
10.1. How CAUHOI2025.UK.COM Can Help
CAUHOI2025.UK.COM offers a wealth of knowledge and expertise to help you navigate the intricate world of football finance. Whether you’re a club executive, investor, or simply a passionate fan, our platform provides valuable insights and resources to enhance your understanding.
10.2. Explore Further Insights
To delve deeper into specific areas of interest, we invite you to explore related articles and resources on CAUHOI2025.UK.COM. From detailed analyses of revenue streams to expert opinions on financial regulations, our platform is your go-to source for comprehensive information on football finance.
FAQ: Football Club Finances
Q1: What are the main sources of revenue for a football club?
A1: The main sources of revenue for a football club include broadcasting rights, matchday and ticketing, commercial activities, and the transfer market.
Q2: How do broadcasting rights contribute to a club’s revenue?
A2: Broadcasting rights are a significant source of revenue, with broadcasters paying for the rights to broadcast league games, and clubs receiving a portion of this revenue.
Q3: Why is matchday income important for football clubs?
A3: Matchday income, including ticket sales and concessions, contributes significantly to a club’s revenue, though its share has decreased over time due to increased broadcasting revenue.
Q4: What commercial activities generate revenue for football clubs?
A4: Commercial activities include income from sponsors, merchandising, tours, and friendly matches, which can contribute a substantial portion of a club’s revenue.
Q5: How does the transfer market impact a football club’s finances?
A5: The transfer market involves the buying and selling of players, with transfer fees contributing to both revenue and expenses for clubs.
Q6: Are most football clubs profitable?
A6: Profitability varies among football clubs, with many clubs in top leagues making a loss despite generating significant revenue.
Q7: What is Financial Fair Play (FFP) and how does it affect clubs?
A7: FFP regulations aim to ensure clubs spend responsibly and balance their spending with their income to avoid accumulating unsustainable debt.
Q8: How do clubs manage their budgets to meet financial targets?
A8: Clubs manage their budgets by defining revenue and cost parameters, controlling payroll, and balancing sales and purchases in the transfer market.
Q9: What strategies can clubs use to manage player costs effectively?
A9: Strategies include investing in youth academies, smart scouting, negotiating favorable contracts, and strategically selling players.
Q10: What role does fan engagement play in a football club’s commercial success?
A10: Engaging with fans through online and offline channels helps clubs build a strong CRM, understand their audience, and drive commercial success.
Ready to explore more insights into the financial workings of football clubs? Visit CAUHOI2025.UK.COM today to discover in-depth articles, expert analysis, and valuable resources. Whether you’re looking to understand revenue streams, financial regulations, or strategic management principles, CAUHOI2025.UK.COM is your ultimate guide. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to enhance your knowledge and gain a competitive edge. Click here to explore CAUHOI2025.UK.COM and start your journey towards financial expertise in the world of football!
For further inquiries, you can reach us at:
Address: Equitable Life Building, 120 Broadway, New York, NY 10004, USA
Phone: +1 (800) 555-0199
Website: CauHoi2025.UK.COM
