Are you curious about the injury trends in football during major tournaments? This article dives into the injury data from FIFA tournaments and the Olympic Games between 1998 and 2012, with a special look at the 2012 season. Discover how injury rates varied across tournaments and the factors influencing these trends, and learn how CAUHOI2025.UK.COM can provide further insights. Explore injury surveillance, sports medicine, and football safety.
Understanding Football Injuries in FIFA Tournaments: A 1998-2012 Analysis
Football, or soccer as it’s known in the United States, is a sport loved and played by millions worldwide. However, it also comes with its share of injuries. The Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) recognized this early on and started systematically documenting player injuries during the 1998 FIFA World Cup. This initiative has continued through 2012, encompassing 51 FIFA tournaments and four Olympic Games. Analyzing this data can provide valuable insights into the frequency, characteristics, and circumstances surrounding these injuries, which can lead to better prevention strategies.
The study of football injuries isn’t just about counting incidents. It’s about understanding how and why these injuries occur. Long-term injury surveillance allows for monitoring changes over time, relating them to the game’s evolution, modifications in playing styles, rule changes, or the introduction of new equipment or playing surfaces. This comprehensive approach is vital for making informed decisions that can protect players and enhance the overall quality of the sport.
Why Is Injury Surveillance Important?
Injury surveillance serves as the foundational step in injury prevention. According to a study by Fuller et al. in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, effective injury prevention strategies are built upon a solid understanding of injury patterns and risk factors. By collecting and analyzing data on injuries, sports organizations can identify specific areas of concern and implement targeted interventions to reduce the risk of injury.
The Methodology Behind Injury Reporting
FIFA developed an injury-reporting system for documenting football injuries during tournaments. This system has been implemented in all FIFA competitions since 1998 and in the football tournaments of the Olympic Games since 2000. The injury definition and data collection procedures align with the respective consensus statement, ensuring consistency and reliability.
What Constitutes an Injury?
An injury is defined as any physical complaint, including concussion, incurred during a match that receives medical attention from the team physician, regardless of whether it leads to absence from the match or training. This broad definition ensures that all incidents are captured, providing a comprehensive view of player health.
Data Collection Procedures
During a pre-tournament instructional meeting, team physicians are asked to report all injuries that occurred during the matches and are trained on how to complete the injury report forms. The injury report form is designed to capture essential details about each incident, including:
- Time of injury (minute in the match)
- Injured body part and type of injury
- Circumstances (non-contact, contact, and foul play)
- Consequences of injury (referee’s sanction, treatment, and time-loss in training or match)
By collecting this detailed information, FIFA aims to gain a thorough understanding of the factors contributing to injuries in football.
Key Findings: Injury Incidence and Characteristics
The study included all FIFA World Cups, FIFA Confederations Cups, and the football tournaments of the Olympic Games from 1998 to 2012. A total of 1681 matches were played, equivalent to 55,473 player-hours. Team physicians completed and returned 3091 injury report forms, covering 51,001.5 player-hours, to the FIFA Medical Officers. The average response rate was an impressive 92%.
Overall Injury Incidence
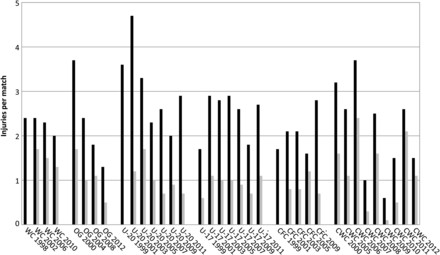
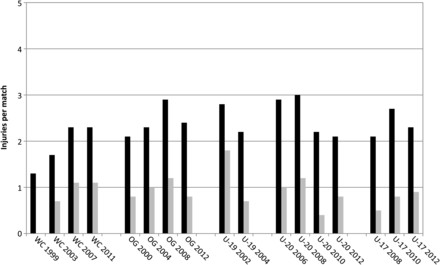
A total of 3944 injuries were reported from 1546 matches, which translates to an incidence of 77.3 injuries per 1000 player-hours or 2.6 injuries per match. The injury rate varied between 1.9 (FIFA Women’s World Cups) and 3 (FIFA U20 World Cups) injuries per match in the different types of tournaments. The incidence was generally lower in tournaments for female players compared with the respective tournaments for male players, except for the Olympic Games.
Body Part Affected
Most injuries affected the lower extremity (70%), followed by injuries to the head and neck (15%), trunk (8%), and upper extremity (7%). The ankle (19%), lower leg (16%), and head/neck were the predominantly injured body parts in almost all types of tournaments.
Types of Injuries
The most common injuries were contusions (55%), sprains (15%), and strains/muscle fiber ruptures (10%). In total, 81 injuries were diagnosed as concussion, 59 as ligament rupture, and 63 as fracture.
Contact vs. Non-Contact Injuries
Most injuries were sustained during contact with another player, while 20% of all injuries were due to non-contact activities. Almost half (47%) of the contact injuries were caused by foul play based on the judgement of the team physician.
Time-Loss Injuries: Impact on Players
Information regarding time-loss from sport after injury was available for 3307 (84%) injuries in 1424 matches. Almost half of the injuries (47%) were expected to prevent the player from participating in a match or training. The incidence of time-loss injuries was highest (1.5 per match) in the FIFA World Cups and lowest (0.7 per match) in the FIFA U17 Women’s World Cups.
Duration of Absence
A total of 1225 (37%) injuries were expected to prevent players from participating in a match or training for up to 1 week, a further 152 (5%) for 8–28 days, and 61 (2%) for more than 29 days. Injuries seemed to be more severe in the FIFA World Cups and the Club World Cups, and less severe in the FIFA U17 Women’s World Cups than in other tournaments.
Trends in Injury Incidence Over Time
The trend of injury incidence over time in different tournaments of male and female players showed interesting patterns. For male players, the average number of injuries per match decreased in the FIFA World Cups and in the football tournaments of the Olympic Games from 1998 to 2012. For female players, the opposite trend was observed in the FIFA Women’s World Cups and the Olympic Games.
What Does This Mean?
These changes were mainly due to changes in the frequency of contact injuries, while the incidence of non-contact injuries remained constant. Stricter refereeing may be one explanation for the decrease in contact injuries of male players.
Diving Deeper: The 2012 Olympic Games
Focusing on the 2012 Olympic Games in London, it’s evident that injury surveillance played a crucial role in understanding the specific challenges faced by athletes during this event. The data collected provided a snapshot of the types of injuries most prevalent and the circumstances under which they occurred. This information is invaluable for developing targeted prevention strategies.
Injury Rates in 2012 Olympics
The study showed that the incidence of injuries in the football tournaments of the Olympic Games decreased from 3.74 injuries per match in 2000 to 1.80 injuries per match in 2012 for male players. For female players, there was an increase from 2.13 injuries per match in 2000 to 2.88 injuries per match in 2008.
Key Factors Influencing Injury Rates
Several factors could have influenced these trends, including:
- Refereeing: Stricter refereeing in men’s tournaments may have reduced contact injuries.
- Playing Style: Women’s tournaments saw a more physical playing style, leading to increased contact injuries.
- Training and Preparation: Advances in training techniques and athlete preparation could have contributed to the overall decrease in injury rates.
The Impact of Rule Changes and Refereeing
One notable finding from the study is the influence of rule changes and refereeing on injury rates. Specifically, the reduction in head injuries after the International Football Association Board gave referees the authority to severely sanction injurious fouls, such as intentional elbows to the head, is significant.
How Stricter Refereeing Reduces Injuries
Stricter refereeing can deter players from engaging in dangerous behavior, reducing the likelihood of contact injuries. This is particularly important in preventing severe injuries like concussions, which can have long-term consequences for players.
The Role of Fair Play
Promoting fair play is another critical aspect of injury prevention. Encouraging players to respect the rules of the game and avoid unnecessary contact can help create a safer environment for everyone.
Gender Differences in Injury Patterns
The study also highlighted some notable gender differences in injury patterns. For example, head/neck injuries were significantly more frequent in female than in male players (17% vs 14% of injuries). Additionally, female players incurred significantly more concussions than their male counterparts.
Why These Differences?
Several factors could contribute to these differences, including:
- Physical Characteristics: Differences in muscle strength, body composition, and hormonal factors may influence injury risk.
- Playing Styles: As noted earlier, women’s tournaments have seen a shift towards a more physical playing style, which could increase the risk of certain types of injuries.
- Protective Gear: Differences in the use of protective gear, such as headgear, could also play a role.
Addressing Non-Contact Injuries
While contact injuries are often the focus of attention, non-contact injuries also represent a significant concern. These injuries, which account for 20% of all reported incidents, can be particularly challenging to prevent.
Common Causes of Non-Contact Injuries
Non-contact injuries are often caused by factors such as:
- Muscle Imbalances: Weak or imbalanced muscles can increase the risk of strains and tears.
- Poor Conditioning: Inadequate physical conditioning can make players more susceptible to injury.
- Environmental Factors: Playing surfaces, weather conditions, and other environmental factors can also contribute to non-contact injuries.
Prevention Strategies
To address non-contact injuries, sports organizations and teams can implement strategies such as:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: These programs should focus on strengthening key muscle groups, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall physical conditioning.
- Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines: These routines can help prepare the body for activity and reduce the risk of muscle strains.
- Monitoring Player Fatigue: Fatigue can increase the risk of non-contact injuries, so it’s essential to monitor players for signs of fatigue and adjust training schedules accordingly.
What This Means for Clinical Practice
The findings from this study have several important implications for clinical practice. First and foremost, they underscore the importance of injury surveillance as a tool for identifying trends and patterns in football injuries.
The Need for Targeted Prevention Strategies
By understanding the specific types of injuries that are most prevalent in different tournaments and player populations, clinicians can develop targeted prevention strategies to reduce the risk of injury. This may involve implementing new training protocols, modifying rules, or improving the quality of playing surfaces.
Educating Referees and Players
Education is also a critical component of injury prevention. Referees should be educated on their influence on injury rates, and players should be taught how to play safely and avoid unnecessary contact.
Reducing the Number of Matches
Finally, reducing the number of matches played, especially for FIFA World Cup and FIFA Club World Cup players, might contribute to a reduction in injury rates. Overuse injuries are a common concern in football, and limiting the number of matches can help prevent these types of injuries.
The Road Ahead: Future Research and Injury Prevention
While this study provides valuable insights into football injuries, there is still much work to be done. Future research should focus on:
- Risk Factors for Non-Contact Injuries: More research is needed to identify the specific risk factors for non-contact injuries, particularly in FIFA World Cup and FIFA Club World Cup players.
- Injury Mechanism: Detailed studies on injury mechanisms can help identify the specific movements and situations that lead to injury.
- Refereeing in Injury Situations: Analyzing how referees handle injury situations can help identify opportunities for improvement.
By continuing to study and analyze football injuries, we can create a safer and more enjoyable sport for players of all ages and skill levels.
CAUHOI2025.UK.COM: Your Go-To Resource for Sports Injury Information
Navigating the complexities of sports injuries can be daunting. That’s where CAUHOI2025.UK.COM comes in. We provide clear, concise, and reliable information on a wide range of sports-related health topics.
Why Choose CAUHOI2025.UK.COM?
- Expert-Backed Information: Our content is thoroughly researched and reviewed by experts in sports medicine and related fields.
- Easy-to-Understand Language: We break down complex medical concepts into simple, accessible language.
- Comprehensive Coverage: From injury prevention to treatment and rehabilitation, we cover all aspects of sports-related health.
Explore More on CAUHOI2025.UK.COM
Ready to dive deeper into the world of sports injuries? Visit CAUHOI2025.UK.COM today to explore a wealth of resources, including:
- In-depth articles on specific injuries: Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for common sports injuries.
- Tips for injury prevention: Discover strategies for reducing your risk of injury.
- Expert advice on rehabilitation: Get guidance on how to recover from an injury and return to sport safely.
At CAUHOI2025.UK.COM, we’re committed to providing you with the information you need to stay healthy and active. Explore our site today and take control of your sports-related health!
Are you struggling to find trustworthy answers to your health and wellness questions? Do you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information available online? CAUHOI2025.UK.COM is here to help. Our team of experts provides clear, concise, and evidence-based answers to your most pressing questions. Whether you’re curious about injury prevention, treatment options, or general health advice, we’ve got you covered.
Have more questions about sports injuries or other health concerns? Don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Equitable Life Building, 120 Broadway, New York, NY 10004, USA or call us at +1 (800) 555-0199. You can also visit our website at CAUHOI2025.UK.COM to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is injury surveillance in football?
Injury surveillance is the systematic collection and analysis of data on injuries occurring in football matches and tournaments. -
Why is injury surveillance important?
It helps identify trends, patterns, and risk factors associated with injuries, which can inform prevention strategies. -
What was the main finding of the 1998-2012 FIFA injury study?
The study found that injury rates varied across different FIFA tournaments and that trends in injury incidence changed over time for both male and female players. -
How did refereeing affect injury rates?
Stricter refereeing was associated with a decrease in contact injuries, particularly in men’s tournaments. -
What were the most common types of injuries reported?
Contusions, sprains, and strains/muscle fiber ruptures were the most common types of injuries. -
Which body part was most frequently injured?
The lower extremity was the most frequently injured body part. -
How did injury rates differ between men’s and women’s tournaments?
Injury rates were generally lower in women’s tournaments, except for the Olympic Games. -
What is a time-loss injury?
A time-loss injury is an injury that prevents a player from participating in a match or training. -
What can be done to prevent non-contact injuries?
Strategies include comprehensive training programs, proper warm-up and cool-down routines, and monitoring player fatigue. -
Where can I find more information about sports injuries?
Visit CauHoi2025.UK.COM for clear, concise, and reliable information on sports-related health topics.
 Male Football Injuries
Male Football Injuries
 Female Football Injuries
Female Football Injuries

