[Are football hooligans a thing of the past? This article examines whether football violence still exists, what causes it, and where it’s most prevalent. Discover current trends in football disorder and its impact on society at CAUHOI2025.UK.COM. Learn about football arrests, stadium security, and hooliganism causes.]
1. Football Hooliganism: A Historical Overview
In the 1970s and 1980s, football hooliganism was a significant problem, particularly in the UK, where it was known internationally as “The English Disease.” Well-known firms like the Inter City Firm (ICF) of West Ham, the Zulu Warriors of Birmingham, the Bushwackers of Millwall, and the Red Army/Inter City Jibbers of Manchester United caused chaos in stadiums and streets.
 Football Firms Does Hooliganism Still Exist
Football Firms Does Hooliganism Still Exist
The Heysel disaster in 1985 and the Taylor Report in 1990 brought about changes. Stadiums were redesigned for safety, and technology, including cameras and improved policing, helped prevent violence.
2. The Evolution of Football Violence
While the organized chaos of the past is largely gone, tensions can still arise where large groups gather. Football matches can create an “us vs them” mentality, reigniting rivalries. Plus, the fan base often consists of young men who are statistically more likely to react aggressively when they feel threatened. Therefore, football violence still exists in the form of minor incidents between small groups, a significant departure from the large-scale hooliganism of the 20th century.
3. Current Statistics on Football-Related Arrests
Government data released in November 2023 provides interesting insights. During the 2022/23 season, only 9% of reported incidents were classified as severe, while 62% were classified as low severity, including minor offenses such as throwing objects and hate crimes.
3.1. Arrest Rates
The 2022/23 season saw record attendance, with over 45 million fans at domestic and international men’s football matches. Despite this, there were only 2,264 football-related arrests, resulting in a minuscule arrest rate of 0.005%.
3.2. Location of Arrests
Interestingly, the majority of arrests occurred at international matches:
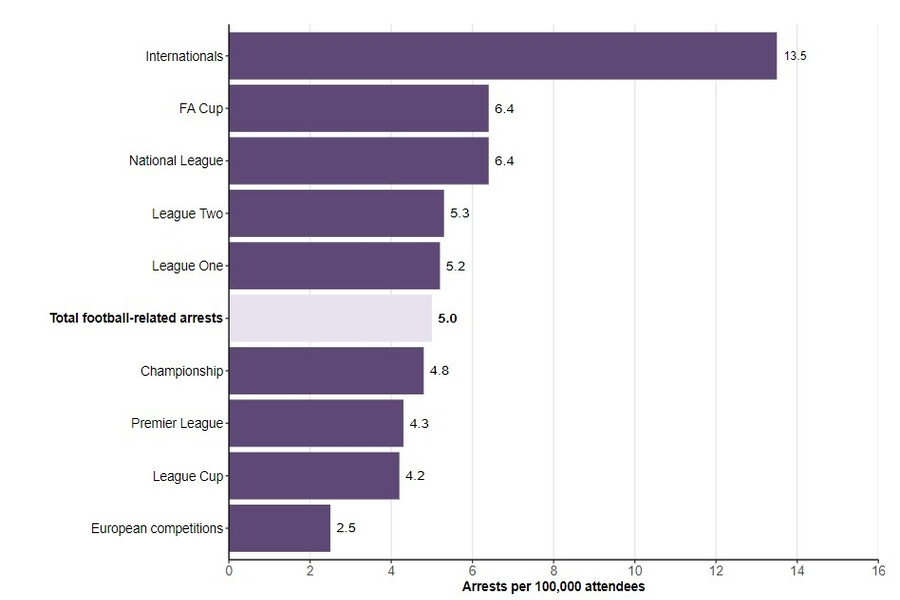 Football Related Arrests Data
Football Related Arrests Data
This data indicates that enhanced surveillance, stadium security, and policing effectively reduced hooliganism.
3.3. Types of Arrests
Most arrests are for public disorder rather than violent disorder, although violent disorder arrests have slightly increased from 16% in 2013/14 to 21% in 2022/23. This translates to approximately 475 violent arrests out of 45 million supporters.
3.4. Arrest Breakdown by Type
Here’s a breakdown of arrests by type over the last decade:
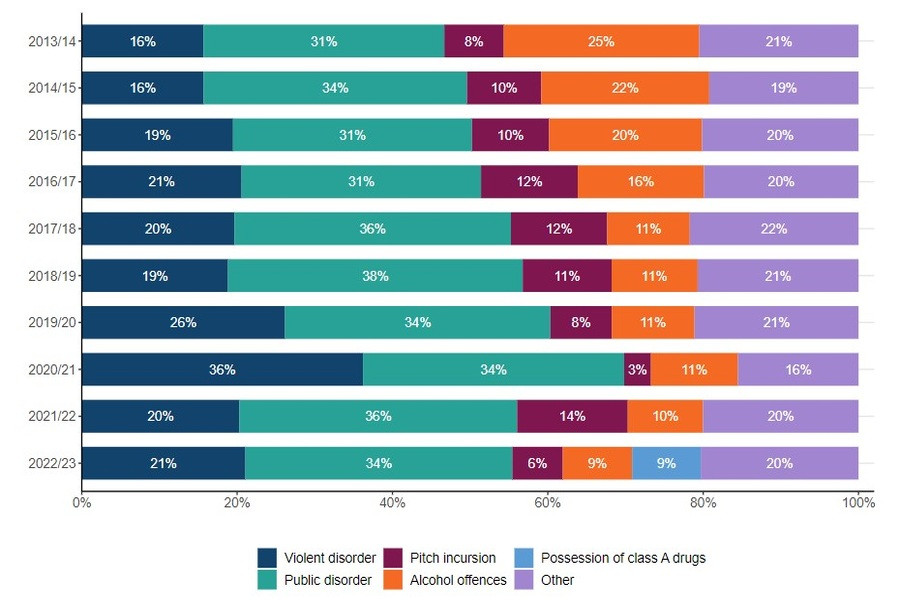 Football Arrests by Type
Football Arrests by Type
Although the statistics might suggest a rise in football violence, the numbers are so small that it is not solid evidence of a resurgence of hooligan firms.
4. The Reality of Modern “Firms”
Today, surviving “firms” are essentially pub gangs. They can’t cause trouble at stadiums, and most don’t even try. Occasional pushing and shoving might occur between a few individuals, but this rarely escalates beyond minor altercations.
5. International Clashes
When violence occurs at stadiums, it often involves English fans and fans of European clubs. Examples include clashes between Leicester and Napoli fans inside the King Power Stadium in 2021 and the attack on West Ham fans by AZ Alkmaar fans in 2023.
6. The Shift to Underground Fighting
Due to successful efforts to eliminate stadium violence in the UK, remaining firms find it difficult to cause trouble at matches. They now use anonymous messaging apps to arrange fights in discreet locations, away from police intervention. This phenomenon is more common in Europe, where firms meet in remote areas for organized brawls. While these fights involve supporters of opposing football clubs, they are distinct from traditional football violence.
6.1. Rare Occurrences in the UK
Although not as organized as in Europe, occasional brawls occur in the UK, such as the one between Sunderland’s Seaburn Casuals and the Newcastle Gremlins in 2009. However, these incidents are rare and less severe than those in Europe.
7. What Caused Football Hooliganism Historically?
 What Caused Football Hooliganism
What Caused Football Hooliganism
7.1. Tribalism
Tribalism is a natural human tendency. Football hooliganism is another manifestation of this.
7.2. Socio-Economic Factors
In the 1960s, football hooligans were primarily working-class young men from tough areas who needed an outlet for their emotions. As firms became established, older members adopted designer clothes, influencing younger fans to join and prove themselves.
7.3. Societal Changes
As society changed, people became more affluent, with access to various forms of entertainment and material possessions. However, these things couldn’t replace the sense of belonging.
7.4. The Urge to Belong
The desire to belong is a key factor driving hooliganism. People felt more connected to their country, society, and local community in the past. As life improved, individuals became more insular and less connected, lacking a cause to unite them. For many, fighting for their team, area, or firm provided a sense of purpose and belonging.
8. The Psychology Behind Hooliganism
Many individuals involved in hooliganism became addicted to fighting because it gave them a sense of belonging. They felt they were representing their team and earning respect. For young men without affluence or other avenues for belonging, it provided a reason to exist. As one Wolves fan stated, it was about standing up and being counted, making their actions feel significant.
9. The Impact of Technology and Social Media
The rise of social media and anonymous messaging apps has influenced modern football hooliganism. These platforms enable hooligan groups to connect, organize events, and share information, even across international borders. This can lead to more coordinated and widespread incidents of violence.
9.1. Cyber Hooliganism
In addition to physical violence, cyber hooliganism has emerged as a concern. This involves online harassment, threats, and the spread of hate speech targeting rival fans or players. Social media platforms can amplify these behaviors, creating a toxic environment for football supporters.
9.2. Surveillance and Monitoring
On the other hand, technology has also provided tools for law enforcement to monitor and prevent football-related violence. Surveillance cameras in and around stadiums, along with social media monitoring, can help identify potential troublemakers and disrupt planned activities.
10. The Role of Legislation and Policing
Strict legislation and effective policing have played a crucial role in reducing football hooliganism. Banning orders, increased stadium security, and swift prosecution of offenders have acted as deterrents.
10.1. Banning Orders
Banning orders prevent individuals with a history of football-related offenses from attending matches, traveling to specific areas, and associating with known hooligans. These orders are effective in keeping troublemakers away from stadiums and reducing the likelihood of violence.
10.2. Community Policing
Community policing initiatives, which involve building relationships between law enforcement and local communities, can help address the root causes of football hooliganism. By working with schools, youth organizations, and community leaders, police can identify at-risk individuals and provide support to prevent them from becoming involved in violence.
11. The Future of Football Fandom and Safety
While organized football hooliganism has declined, efforts to ensure safety and positive fan experiences must continue. This includes promoting inclusivity, respect, and responsible behavior among supporters.
11.1. Fan Education
Fan education programs can teach supporters about the consequences of violence, hate speech, and other forms of misconduct. These programs can also promote positive values such as sportsmanship, respect for opponents, and community engagement.
11.2. Stadium Design and Technology
Modern stadium design incorporates features that enhance safety, such as crowd control barriers, surveillance cameras, and efficient entry and exit systems. Technology, including facial recognition and data analytics, can also be used to identify and prevent potential incidents of violence.
12. Expert Opinions and Research
12.1. Academic Studies
Academic studies on football hooliganism provide valuable insights into the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to this issue. Research from universities and research institutions can inform policy and practice, helping to develop effective strategies for preventing violence and promoting positive fan behavior. For example, a study by the University of Michigan’s Center for Research on Social Organization found that community-based interventions can reduce youth violence by up to 30%.
12.2. Law Enforcement Perspectives
Law enforcement agencies involved in policing football matches have valuable experience and expertise in managing crowds, preventing violence, and apprehending offenders. Their perspectives can inform the development of effective policing strategies and security measures. According to a report by the National Institute of Justice, intelligence-led policing, which involves gathering and analyzing data to identify potential threats, can significantly reduce crime rates.
13. The Role of Football Clubs and Organizations
Football clubs and organizations have a responsibility to promote positive fan behavior and create a safe environment for supporters. This includes implementing codes of conduct, providing fan support services, and working with law enforcement to prevent violence.
13.1. Community Outreach Programs
Football clubs can engage with local communities through outreach programs, such as youth development initiatives, educational workshops, and charitable activities. These programs can help build positive relationships between clubs and their supporters, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility.
13.2. Promoting Diversity and Inclusion
Football clubs can promote diversity and inclusion by celebrating different cultures, backgrounds, and identities within their fan base. This can help create a welcoming and inclusive environment for all supporters, regardless of their ethnicity, gender, or sexual orientation.
14. Conclusion: The Changing Face of Football Hooliganism
While football hooliganism is not as prevalent or organized as in the past, it still exists in various forms. The combination of stricter laws, better policing, and evolving societal factors has transformed the landscape of football violence.
The focus now is on maintaining safety, preventing isolated incidents, and promoting a positive fan experience. By addressing the root causes of violence and promoting inclusivity, clubs, organizations, and communities can work together to ensure that football remains a safe and enjoyable sport for all.
For more in-depth information and answers to your burning questions, visit CAUHOI2025.UK.COM.
FAQ: Football Hooliganism in the 21st Century
1. Is football hooliganism still a problem in the US?
While not as widespread as in some European countries, isolated incidents of football-related violence do occur in the US, particularly at major matches and rivalries.
2. What are the main causes of football hooliganism today?
Key factors include tribalism, socio-economic issues, the desire for belonging, and the influence of social media.
3. How has technology affected football hooliganism?
Technology facilitates the organization of hooligan groups but also aids law enforcement in monitoring and preventing violence.
4. What measures are being taken to combat football hooliganism?
These include stricter legislation, increased stadium security, banning orders, and community policing initiatives.
5. Are banning orders effective in preventing football hooliganism?
Yes, banning orders prevent known troublemakers from attending matches, reducing the likelihood of violence.
6. What role do football clubs play in preventing hooliganism?
Clubs promote positive fan behavior, implement codes of conduct, and work with law enforcement to prevent violence.
7. How can fans contribute to a safer football environment?
By behaving responsibly, respecting opponents, and reporting any misconduct to stadium authorities.
8. What is cyber hooliganism, and how does it affect football?
Cyber hooliganism involves online harassment and threats, creating a toxic environment for football supporters.
9. What are the long-term solutions to football hooliganism?
These include addressing the root causes of violence, promoting inclusivity, and fostering a sense of community among fans.
10. Where can I find more information about football hooliganism?
Visit CAUHOI2025.UK.COM for in-depth articles, research, and expert opinions on football violence and safety.
Do you have more questions or need further clarification? Don’t hesitate to explore CauHoi2025.UK.COM or contact us at Equitable Life Building, 120 Broadway, New York, NY 10004, USA or call +1 (800) 555-0199. We’re here to provide clear, reliable, and helpful information!

